- Good for: Eyesight, growth, appetite and taste.
- Signs of deficiency: Night-blindness
- RDA: 800 micrograms(mcg)
- Good sources: Liver, cod liver oil, carrots, green leafy vegetables, egg yolks, enriched margarine, milk products, and yellow fruits.
- Poisoning: Is fat-soluble and so is stored in the body for a long time, especially in pregnancy. An overdose may be dangerous.
- Destroyed by: Fatty acids.
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin which means it can be dissolved in fat. Is carried through the body by fat.
The body can store in fat tissue. Getting too much can be harmful.
This can come from animal sources such as:
- Eggs
- Fortified milk
- Liver
- Oils of some fish
This form of Vitamin A is called retinal or retinol.
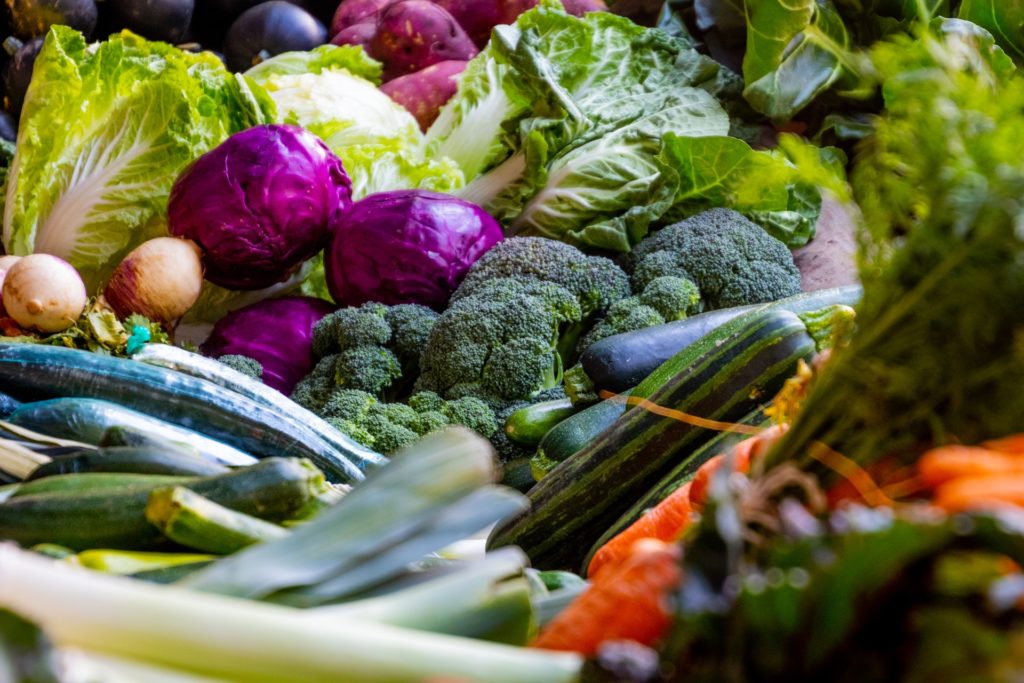

Is also found in plants. This form is called carotenoids. Substances such as beta-carotene are converted from carotenoids into vitamins in the body.
Beta-carotene is one of the most common carotenoids. Carotenoids are pigments found in deep orange, red, and yellow fruits and vegetables. They are also found in many dark-green leafy vegetables, such as:
- Carrots
- Pumpkin and other squashes
- Sweet potatoes
- Cantaloupe
- Broccoli
- Spinach
Vitamins A is essential to preserve sight.
This vitamins is needed to convert the light that reaches your eye into an electrical signal that can be sent to your brain.
In fact, one of the first symptoms of vit. A deficiency may be night blindness, known as nictalopia.
Night blindness occurs in people with vit. A deficiency, since this vitamins is an important component of the rhodopsin pigment.
Rhodopsin is found in the retina of the eye and is extremely sensitive to light.
© Copyright – Hector Sectzer